The Pythagorean Theorem is one of the great advances in mathematics, a theory developed by Pythagoras and the group who followed him, known as Pythagoreans. The popularity of the Pythagorean Theorem is unmatched and today is considered one of the fundamental formulas in geometry and mathematics in general. The simplicity with which it relates the different sides of a right triangle opens the door for a huge number of applications that can be developed based on this theorem.
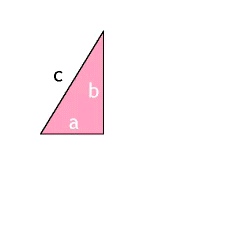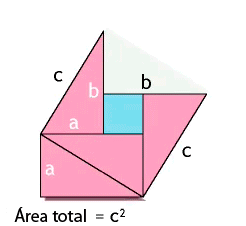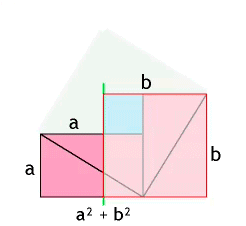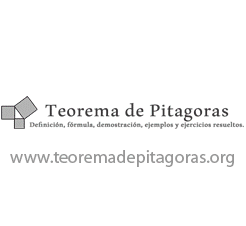
Pythagoras, with the help of his Pythagoreans, discovered that if we square each of the two legs in a right triangle and add them together, the value will be the same as if we squared the hypotenuse of the same triangle. We should remember that a leg is one of the sides that “touches” the right angle of the triangle on one end; there are only two legs in every right triangle and it is impossible for there to be just one or more than two as this would deform the shape and no longer be a triangle. Likewise, the hypotenuse is the remaining side which is always across from the right angle. We can also recognize the hypotenuse because of its size, since it is the longest side of a right triangle.
The discovery of the Pythagorean Theorem opened up a new world in mathematics known at that time and even today it continues to surprise us and serve as a base for new theories that help humanity delve deeper and deeper into a field as important as math. If you don’t know the Pythagorean Theorem yet or if you are still having difficulties applying it, don’t worry; in our examples section you can find many examples that can help answer your questions.

Be the first to comment on "Pythagorean Theorem"